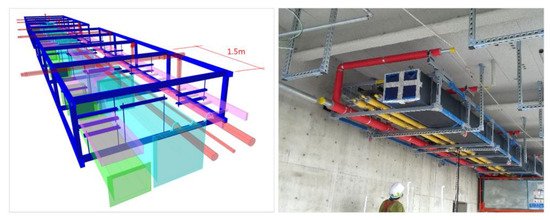
Each year, over 32,000 home fires erupt in the U.S. due to electrical code violations—leading to injuries, fatalities, and billions in property loss. For electrical contractors, this isn’t just a statistic—it’s a wake-up call.
Staying compliant isn’t optional; it’s foundational. And at the center of safe installations is the National Electrical Code (NEC), the gold standard for electrical design and construction across the States.
With the 2025 NEC code updates, big changes are on the horizon—think smarter load management, enhanced GFCI protection, and integration with smart energy systems. These updates don’t just reflect technological progress; they reshape how we plan, coordinate, and execute MEP projects.
But here’s the challenge: the NEC is exhaustive and state-specific. Navigating it manually eats into your time—and your bottom line. That’s where LOD 400 BIM modeling steps up.
By integrating automation and high-detail BIM workflows, contractors can:
- Spot compliance issues early
- Coordinate across trades more efficiently
- Stay ahead of evolving code requirements
As the code evolves, so must your tools. NEC compliance in 2025 isn’t just about knowing the rules—it’s about building smarter from the ground up.
Table of Contents
Pro tip:
Eracore Group delivers LOD 400 precision. Revit-powered modeling with embedded GFCI metadata. Code compliance built into every device. Fewer inspection delays, zero missed details. Meet 2025 NEC updates with confidence.
What’s New in the 2025 National Electrical Code (NEC)?
The 2025 National Electrical Code introduces some of the most impactful changes yet, aimed at elevating electrical safety, promoting smarter energy consumption, and accommodating the growing diversity of renewable systems. These updates reflect a proactive approach to modern electrical demands and reinforce the importance of designing with long-term efficiency and compliance in mind.
Key highlights include:
Expanded GFCI Placement Requirements
The NEC 2025 is raising the bar for electrical safety. GFCI protection—once confined to bathrooms and kitchens—is now required in areas where dampness and risk collide:
- Outdoor outlets
- Basements
- Garages
- Laundry rooms
- Crawl spaces
These spaces are prone to moisture, exposed surfaces, and unpredictable load conditions. Installing GFCIs here isn’t just code compliance—it’s a frontline defense against electrical shock. For contractors, it means recalibrating site inspections and updating default outlet specs across residential and commercial builds.
Load Calculation Changes
What’s moved isn’t minor—Article 220’s relocation to Chapter 1 in Article 120 changes the way electrical professionals reference load calculations across feeders and branch circuits.
Why it matters:
Article indexing affects blueprint reviews and permit documentation
Inaccurate referencing could derail sizing or inspection
Design software and templates may need updates to align with the restructure
Think of it as the first step in a larger NEC streamlining effort. Getting ahead of these changes now will avoid miscommunication and rework down the road.
Energy Management Systems: Code Meets Smarter Power
Energy Management Systems (EMS) are now officially part of the NEC framework. These systems regulate consumption—especially during peak hours—and optimize the behavior of:
- Solar panels
- Battery systems
- EV chargers
This integration supports utility cost savings, grid stability, and emission reduction—all while introducing technical benchmarks for load controls and switching logic. Designers should factor EMS early into spec sheets and coordination meetings, especially for commercial and multi-family projects.
EV & Renewable Standards: Power Goes Both Ways
Bidirectional power is no longer a future concept—it’s a compliance item. Updates to:
- Article 625 (EV charging systems)
- Article 706 (Energy storage systems)
reflect the reality of homes and buildings both drawing and supplying power. That means:
- Chargers must manage two-way flow
- Storage systems must isolate effectively
- Equipment must be grid-safe and fault-tolerant
These aren’t optional upgrades—they’re required features for modern installations.
Why GFCI Compliance Demands More Than Just Symbols
Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) are critical life-saving devices designed to shut off power immediately when electrical faults occur—such as current leakage through water or direct human contact. In moisture-prone environments, their role is non-negotiable. Since their introduction, GFCIs have helped reduce household electrocution fatalities by more than 80%, according to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI).
Despite clear mandates in the National Electrical Code, traditional planning methods still leave room for error:
⚠️ Code-required GFCI outlets may be overlooked in design
⚠️ Devices are sometimes installed without proper documentation
⚠️ Incomplete drawings lead to failed inspections and rework
This is where high-fidelity modeling makes the difference. At LOD 400, GFCI specifications are embedded directly into the electrical model—complete with device metadata, location validation, and installation intent. This level of detail gives field teams, inspectors, and engineers the assurance that code compliance isn’t just represented—it’s reinforced.
For contractors navigating the expanded 2025 NEC placement requirements, LOD 400 BIM offers a proactive, verifiable approach that minimizes risk and keeps projects inspection-ready.
Since the 1970s, Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) have made homes dramatically safer, reducing the risk of fatal electric shock by more than 80%, according to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI). These smart devices instantly trip the circuit when electricity flows where it should not, such as through water or a person, making them silent guardians in high-risk areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets.
Modeling to LOD 400 for Better GFCI Compliance
Generic symbols and callouts aren’t enough anymore. With the expanded scope of GFCI requirements under the 2025 NEC, relying on annotations alone leaves too much room for error. That’s why more contractors are turning to LOD 400 modeling, where every electrical device is fully defined with accurate dimensions and embedded data.
In practice, this means:
- Every receptacle in the model clearly identifies whether it’s GFCI-protected or not.
- GFCI status is stored within the family using structured Revit parameters.
- Quality control shifts from manual review to smart filtering and automated checks.
This isn’t about making models look good—it’s about making them work smarter. When you build compliance into the digital twin, errors get caught before they reach the field.
Why Device-Level Metadata Matters
Meeting NEC 2025 requirements takes more than placing outlets in the right spots. You need to know what kind of outlet it is, what circuit it’s on, and whether it meets code for the environment it’s installed in.
Using Revit parameters at LOD 400, contractors can embed details like:
- GFCI status (Yes/No)
- Circuit and panel assignments
- Manufacturer and model
- Voltage, amperage, and load classification
This makes device tracking easier, schedules more reliable, and field coordination more precise. When inspectors walk onsite, they’re reviewing a design that’s already been validated digitally with no surprises.
The more intelligence you put into your electrical model, the less risk you carry into installation. With LOD 400, contractors can run compliance checks before a single wire is pulled. That means:
- Fewer inspection delays
- Less rework
- Stronger documentation that backs up every outlet placement
Get Your BIM Workflow Ready for NEC 2025
NEC 2025 is clear: compliance is getting more granular. Eracore Group helps contractors stay ahead by integrating device logic and code alignment into every phase of modeling. From GFCI tagging to real-time auditing, our Revit workflows help you build smarter—and pass inspections with confidence.
Looking to tighten compliance or improve your BIM output? Let’s talk shop and get your next project ready for what’s next.
Frequency Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the biggest changes in the electrical code for 2025?
The 2025 update to the National Electrical Code (NEC) brings significant changes that focus on enhanced safety, energy efficiency, and future-ready infrastructure. Key revisions include broader GFCI protection requirements in areas like basements, garages, and outdoor outlets, an organizational shift in load calculation rules with the relocation of Article 220 to Chapter 1 of Article 120, and updated standards for energy management systems. There are also new provisions for EV charging and energy storage systems that account for bi-directional power and smart grid integration.
Why is detailed modeling important for electrical safety?
Detailed modeling plays a crucial role in preventing electrical hazards and ensuring compliance with safety codes. When each component—such as outlets, circuits, and panels—is accurately represented and logically connected, it minimizes the risk of design errors and overlooked code requirements. This precision helps contractors identify potential issues before construction begins, which improves coordination and reduces on-site risks.
How does advanced BIM modeling help meet electrical code requirements?
Advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM), especially at LOD 400, allows contractors to embed compliance data directly into the design. Metadata such as circuit numbers, GFCI status, and voltage ratings are attached to each device, enabling automated checks and accurate reporting. This makes it easier to adhere to the increasingly complex code requirements introduced in NEC 2025 without relying solely on manual documentation.
What risks come from missing details in electrical models?
Advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM), especially at LOD 400, allows contractors to embed compliance data directly into the design. Metadata such as circuit numbers, GFCI status, and voltage ratings are attached to each device, enabling automated checks and accurate reporting. This makes it easier to adhere to the increasingly complex code requirements introduced in NEC 2025 without relying solely on manual documentation.
How can designers ensure their models meet new safety standards?
Designers can ensure compliance with NEC 2025 by modeling to a high level of detail, such as LOD 400, and integrating critical safety metadata into each component. Using Revit parameters to tag devices correctly, running automated code checks, and keeping BIM templates aligned with the latest NEC revisions are all best practices. Staying informed and embedding code logic into the design process helps streamline inspections and supports long-term project safety.